Naira’s Depreciation Blamed on Forex Shortages and High Demand
- Brandon Davis
- July 22, 2023
- Crypto, News
- Crypto, Forex, High Demand, Naira
- 0 Comments
The Nigerian naira’s recent depreciation is caused by forex shortages and high demand, prompting economic concerns and the need for comprehensive solutions.
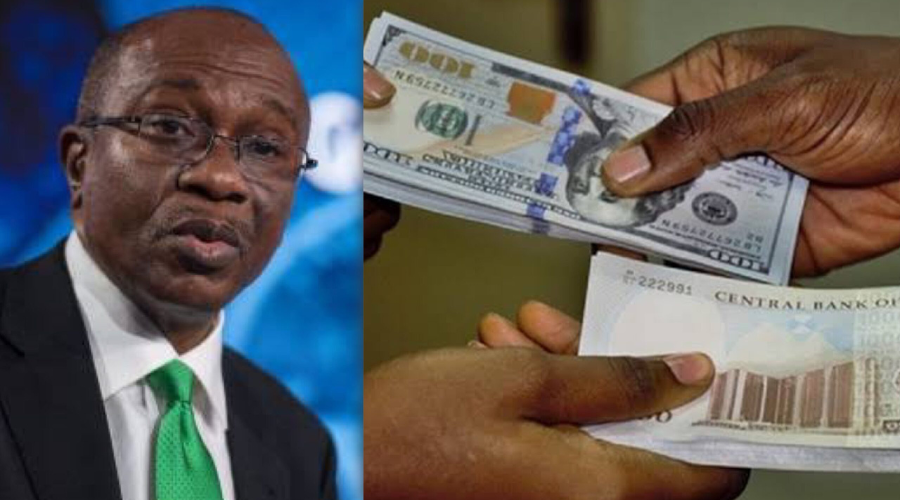
The Nigerian naira’s recent loss in value has been closely linked to foreign exchange shortages on the official market along with a surge in demand for forex. This alarming development has sent shockwaves across the nation, raising concerns and prompting experts to analyze its impact on the economy.

The scarcity of foreign exchange, primarily US dollars, has placed immense pressure on the official market. As a result, the naira’s value has taken a hit, significantly depreciating against major international currencies. This depreciation is cause for worry as it directly affects Nigeria’s import-dependent economy and has wider implications for businesses and citizens alike.
A key driver behind the forex shortages can be attributed to various factors. Firstly, the global economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted international trade and led to a decline in export earnings. This reduction in foreign revenue has limited the availability of foreign exchange for the Nigerian government.
Furthermore, Nigeria’s heavy reliance on oil exports as a major revenue source has made the naira susceptible to fluctuations in global oil prices. Recent instability in oil markets, coupled with OPEC+ production cuts, has negatively impacted the country’s oil earnings. This, in turn, has put additional strain on the forex reserves.
Simultaneously, the rising demand for forex in Nigeria has exacerbated the situation. With a large population and increasing import requirements, the demand for foreign currencies has grown significantly. Individuals, businesses, and even the government itself require foreign exchange for various purposes, such as importing goods, paying off international debts, or funding overseas travel.
However, the limited availability of foreign exchange on the official market has resulted in a thriving parallel market. This alternative market operates outside regulatory frameworks and often offers higher exchange rates, leading to increased market volatility. The existence of a parallel market not only reflects the scarcity of forex but also poses risks such as money laundering and illegal transactions.
To address this crisis, the Nigerian government has taken several measures. The Central Bank of Nigeria (CBN) has introduced policies to control and manage the foreign exchange market effectively. These measures include direct interventions, restrictions on accessing forex for certain imports, as well as the promotion of local production. Additionally, the CBN has encouraged the use of digital platforms for foreign transactions, aiming to increase transparency and track foreign exchange flows.
Nevertheless, experts caution that sustainable solutions to the forex scarcity and naira depreciation require a comprehensive approach. Diversifying Nigeria’s economy and reducing its heavy reliance on oil exports is seen as crucial for long-term stability. Encouraging foreign investments, promoting non-oil sectors such as agriculture and technology, and improving the ease of doing business have been suggested as viable strategies to boost the economy and alleviate the forex shortage.
As the Nigerian government continues to grapple with these challenges, its ability to effectively manage foreign exchange resources and stabilize the naira will be crucial. The success of these efforts will determine Nigeria’s economic trajectory and its future position in the global market.
Takeaway
- Nigerian naira’s depreciation linked to forex shortages and high demand, raising economic concerns.
- Factors: COVID-19 impact on trade, fluctuating global oil prices, and rising local forex demand.
- Parallel market thrives due to limited official market availability, posing risks.
- Government introduces forex control measures, experts suggest diversifying economy and attracting foreign investments for long-term stability.